Visual Reasoning – Concepts for Aptitude
Topic-wise Aptitude Concepts
Visual reasoning is a crucial part of many aptitude tests, especially those used in placements and competitive exams. It involves understanding, analyzing, and interpreting patterns, shapes, or figures presented in a logical sequence or spatial arrangement. This section evaluates a candidate’s spatial intelligence, logical thinking, and pattern recognition ability. Some students jokingly say that it is an eye sight test 😛
Types of Visual Reasoning Questions
Visual reasoning can cover several types of questions. Here are the most common ones:
- Series Completion: You are given a sequence of images or patterns, and you need to determine the next image in the series based on the established pattern.
- Odd-One-Out: You are presented with a group of images or shapes, and you have to identify the one that does not follow the same pattern as the others.
- Mirror Images: These questions involve finding the mirror image of a given shape or design, testing your ability to mentally reverse objects.
- Embedded Figures: You need to find a specific shape or pattern embedded within a larger, more complex figure.
- Paper Folding and Cutting: These questions test your spatial visualization by asking you to determine how a piece of paper folded and cut in a particular way would look when unfolded.
Strategies for Solving Visual Reasoning Questions
- Observe Carefully: Look for repeated patterns or transformations such as rotation, reflection, shading, or resizing.
- Break Down Complex Patterns: Simplify complex shapes into basic components or sub-patterns.
- Analyze the Position of Elements: Pay attention to any changes in the position, orientation, or size of elements.
- Eliminate Incorrect Choices: For multiple-choice questions, use the process of elimination to narrow down your options.
Solved Examples of Visual Reasoning Questions
Example 1: Series Completion
Question: Identify the next figure in the series below.
Figures in Sequence:
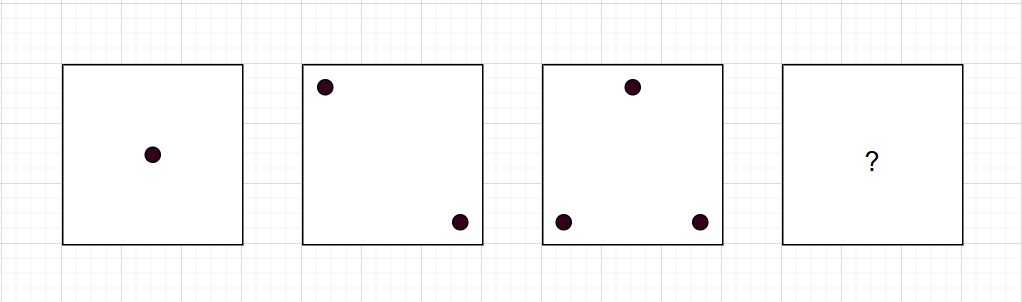
Solution: Observe the pattern in the dots’ arrangement:
- In each figure, the number of dots increases by one.
- The dots also form progressively more complex shapes with each figure.
The next figure would likely be a square with four dots in square shape
Example 2: Odd-One-Out
Question: Choose the odd one out from the following figures.
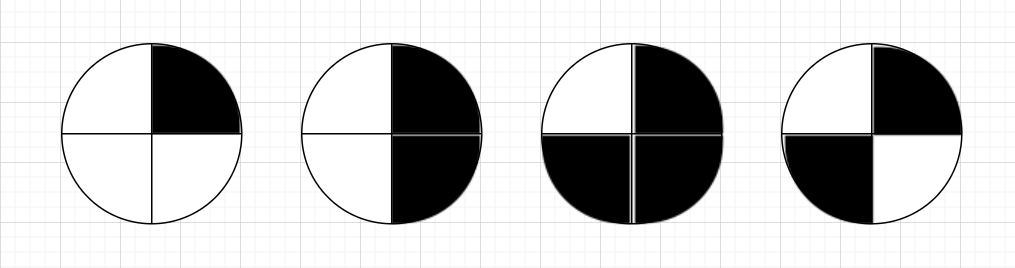
Solution: Observe the shading pattern:
- The first three figures have contiguous (connected) shaded regions.
- In the fourth figure, the shaded quadrants are opposite each other, not connected.
Answer: The fourth figure is the odd one out.
Example 3: Mirror Images
Question: Identify the mirror image of the following figure:
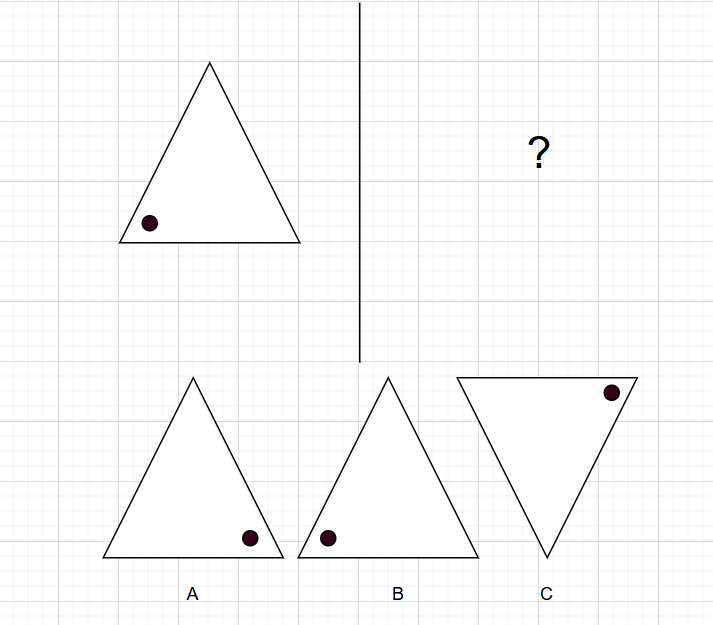
Solution: When a figure is reflected in a mirror, it reverses horizontally.
- In the mirror image, the triangle will still point upwards.
- However, the dot, originally on the left side of the triangle, will now appear on the right side. A is the correct answer.
Example 4: Paper Folding and Cutting
Question: A square piece of paper is folded twice, once horizontally and once vertically, and a small circle is cut out from the corner of the folded paper. What will it look like when the paper is unfolded?
Solution: After two folds, any cut made on one corner of the folded paper will appear on all four corners when the paper is unfolded.
- Since a single circle was cut on the folded paper, there will be four circles, one in each corner, when the paper is unfolded.
Tips for Practicing Visual Reasoning
- Practice with Puzzles: Engaging in puzzles like jigsaw, tangram, and block-building exercises can strengthen your spatial and pattern-recognition skills.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards with different types of patterns and transformations to regularly test yourself.
- Time Your Practice: Since aptitude tests are timed, practice visual reasoning questions under time constraints to improve speed and accuracy.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overlooking Small Details: Missing subtle changes, like a slight rotation, can lead to incorrect answers.
- Rushing Through Patterns: Failing to analyze the pattern thoroughly can lead to missed logical connections.
- Getting Stuck on One Problem: If a question seems too complex, move on and return to it if time permits.
Read concepts and formulas for: Synonym Antonym
LearnTheta is an AI-powered practice platform designed to help students to crack Placement Aptitude Tests: https://www.learntheta.com/placement-aptitude/